Variable costs are costs that do vary with output and they are also called direct costsExamples of typical variable costs include fuel raw materials and. Costs incurred by businesses consist of fixed and variable costs.

Kaplan Bu224 01 Unit 7 Assignment Cost Elements Of A Business Assignments The Unit Kaplan
The change in the total cost when the quantity produced changes by one unit.

. Variable costs change based on the amount of output produced. Costs that vary directly with the level of production. An economy is self-sufficient in production.
Mathematically speaking marginal cost is equal to the change in total cost divided by the change in quantity. 11 20 Fixed cost is a costs that vary with the quanuly of output produced b. Fixed costs are upfront costs that dont change depending on the quantity of output produced.
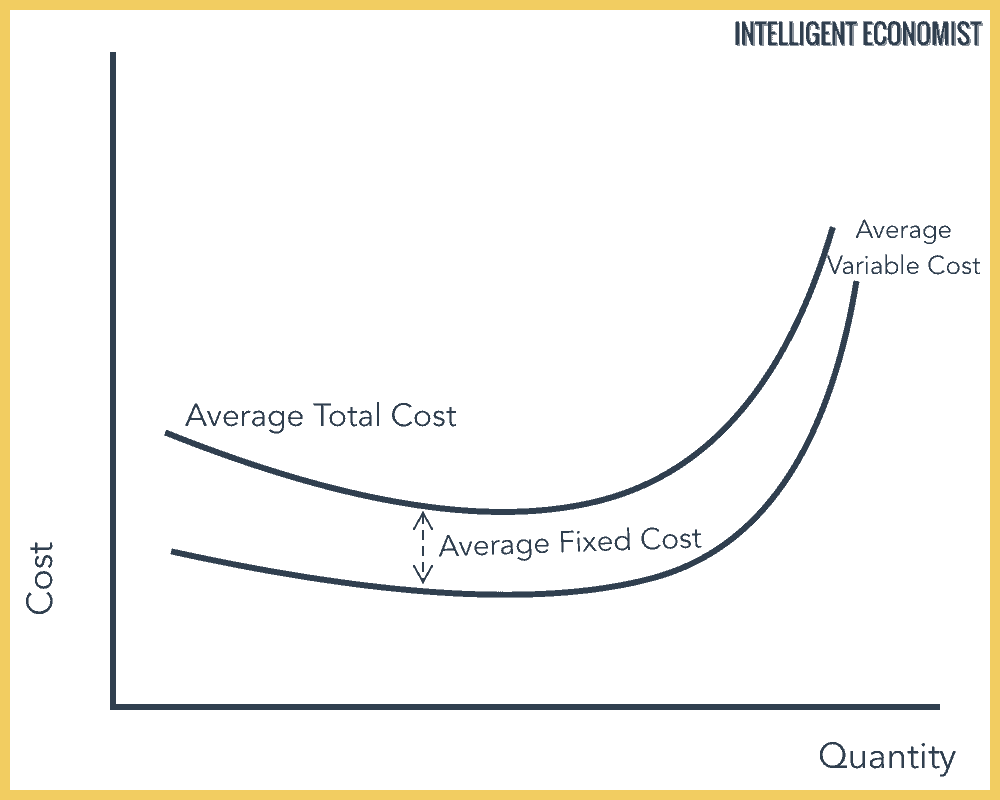
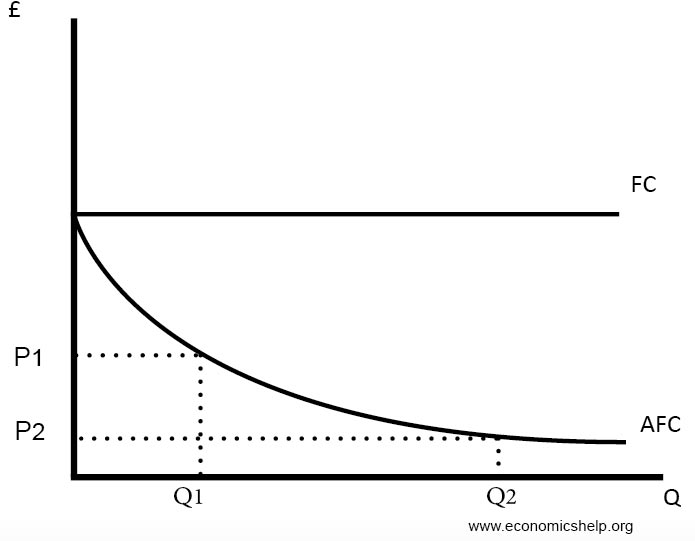
Cost that do not v. None of the above e both b and c 29 Total Physical Product divided by. Costs that do vary with the quantity of output produced VC Total Cost The market value of all the inputs that a firm uses in production TC FCVC Average Fixed Costs Fixed costs divided by the quantity of output AFC FCQ Average Variable Cost Variable costs divided by the quantity of output AVC VCQ Average Total Cost Total cost divided by the quantity of output ATC TCQ.
ATC change in total cost change in. Those costs are called A. Pages 113 This preview shows page 98 -.
Costs do vary quantity output produced tc market. A graph of the costs of production as a function of total quantity produced. In a free market economy firms use.
The quantity at which market price is equal to Sams marginal cost of production. Some costs do not vary with the quantity of output produced. School Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology.
Average total cost ATC is calculated as follows. Also called sunk costs C. As mentioned above variable expenses do not remain constant when production levels change.
Costs that vary with the quantity output produced average fixed cost fixed cost divided by the quantity of output average variable cost variable cost divided by the quantity of output marginal cost the increase in total cost that arises from an extra unit of production ATC TCQ MC change in total costchange in quantity efficient scale. Fixed costs are those that do not. Marginal cost is the cost associated with producing one more unit of output.
Total Variable Cost Total Quantity of Output x Variable Cost Per Unit of Output. Cost that do not vary with the quantity Q of output produced d. Price x quantity - total cost.
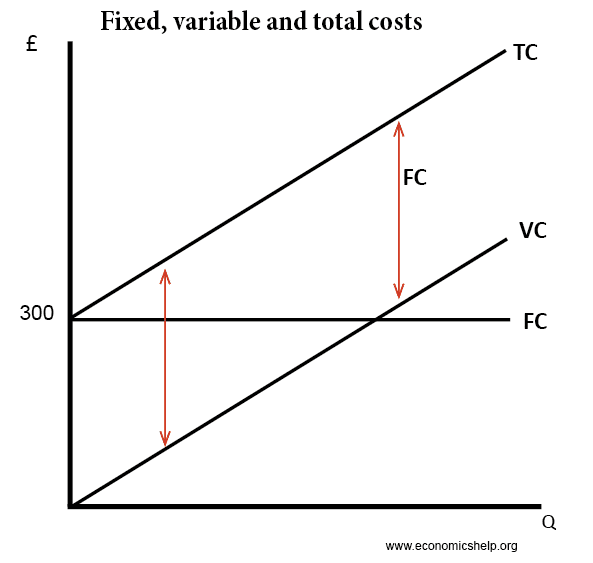
Fixed costs are those that do not vary with output and typically include rents insurance depreciation set-up costs and normal profitThey are also called overheads. School University of British Columbia. Variable and fixed costs.
Also called sunk costs C. Variable vs Fixed Costs in Decision-Making. Fixed costs variable costs.
ATC change in total cost change in quantity of input. Variable costs change with the output. Examples of variable costs include employee wages and costs of raw materials.
Costs that do not vary with the quantity of output. Quantity of output and total cost. Marginal costs vary with the volume of output being produced.
11 20 Fixed cost is a costs that vary with the quanuly of output produced b. ATC total cost quantity of output. Fixed cost divided by the quantity of output.
Pages 32 This preview shows page 19 - 27 out of 32 pages. Fixed costs are large relative to variable costs. Quantity of inputs and total cost.
Course Title ECON 1020. Marginal cost can either be thought of as the cost of producing the last unit of output or the cost of producing the next unit of output. Economies of scale arise when.
Costs of production Fixed and variable costs. Variable cost divided by the quantity of output. Companies incur two types of production costs.
Some costs do not vary with the quantity of output produced. Costs do not vary with quantity output produced VC costs do vary quantity from ECON 1020 at Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology. On the other hand fixed costs are costs that remain.
Variable costs are costs that vary directly with the amount of output. Variable costs may include labor commissions and raw. They are affected by various factors such as price discrimination Price DiscriminationPrice discrimination refers to a pricing strategy that charges consumers different prices for identical goods or services externalities information asymmetry and transaction costs.
Costs that do not vary with the quantity of output produced Costs that vary with. Costs that do vary with the quantity of output produced VC Total cost The from ECON 1020 at Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology. Some costs do not vary with the quantity of output produced.
Course Title MINE 406. Individuals in a society are self-sufficient. The quantity at which market price is equal to Sams marginal cost of production.
Total cost divided by quantity of output produced.
Theory Of Production Cost Theory Intelligent Economist
0 Comments